Information on Career Progression for Healthcare Business Management Professionals.
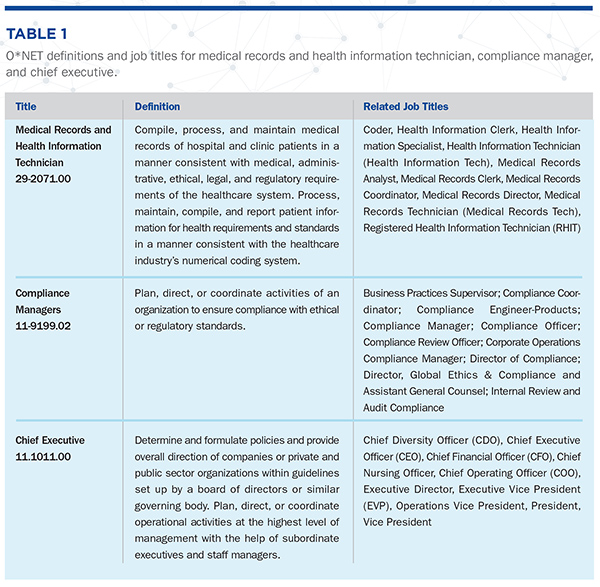
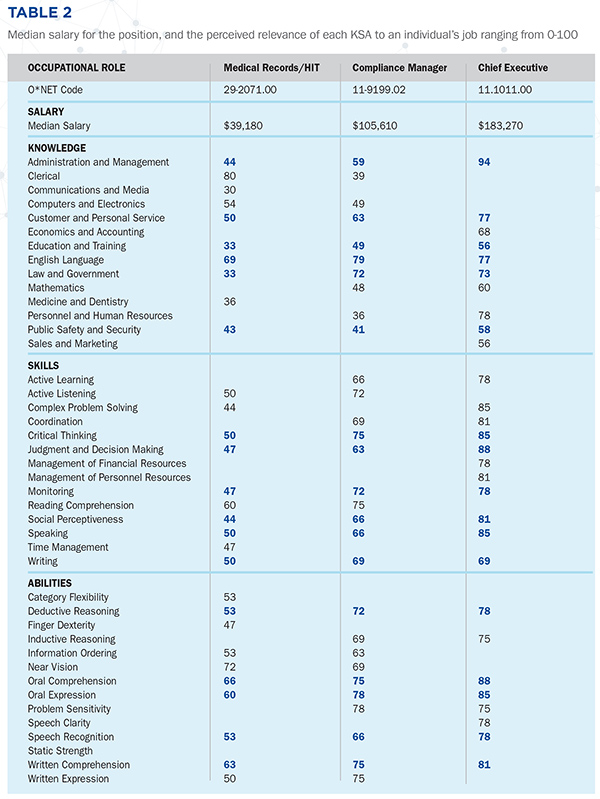
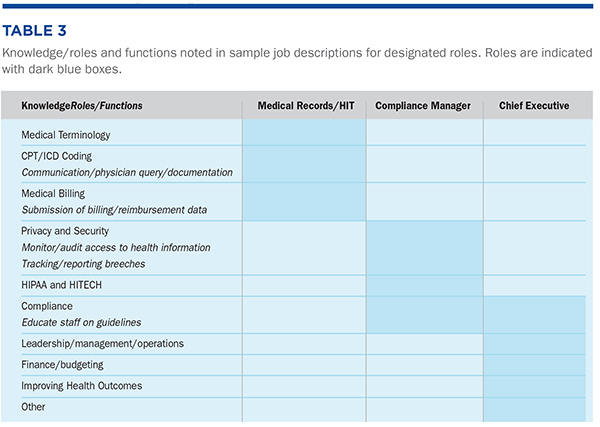
Methods O*NET data is collected by the National Center for O*NET Development and sponsored by the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment, and Training Administration.4 O*NET data are collected from a random sample of practicing healthcare professionals that focus on knowledge (academic areas), skills (capabilities that facilitate learning), and abilities (attributes that influence job performance) (KSAs). O*NET data for the following healthcare business management professional occupational roles are reviewed: medical records and health information technician (Code: 29-2071.00); compliance manager (Code: 11-9199.02); and chief executive (Code: 11.1011.00). Given the lack of a common language and the variety of titles associated with each of these occupational roles, the following definitions from the O*NET database along with a listing of associated job titles are provided in Table 1.5 Results and Discussion Data from Table 2 strongly supports the importance of common employability skills across the career progression for the occupational roles examined: medical records and health information technician, compliance manager, and chief executive. Of the KSAs noted in Table 2, 16 of the 18 that carry across the career progression pathway are common employability skills, as defined by the National Network of Business and Industry Associations (NNBIA) study.6 Using the NNBIA framework, under personal skills: social perceptiveness; applied knowledge: writing, written comprehension, critical thinking; workplace skills: customer and personal service, judgment and decision making, administration and management, deductive reasoning, monitoring; and people skills: communication (English language, speaking, oral comprehension, oral expression, speech recognition). Two KSAs, education and training, and law and government, fall outside the segments defined within the NNBIA framework but are closely related competencies. The KSA categories seem to be related to job-specific tasks included in job descriptions surveyed for each of the occupational roles. Table 3 provides a summary of open access job descriptions for each role accessed via an internet search engine. Comparing these highlighted areas of emphasis with data from the organizational job descriptions, we see that KSAs are directly tied to the specific job tasks for each of the occupational roles under consideration. From the job description data, we see that specific job tasks move from transactional to transformative, and from operational to strategic. This fundamental change in how work is perceived along the career progression pathway demonstrates the importance of the need for training in the common employability skill areas.
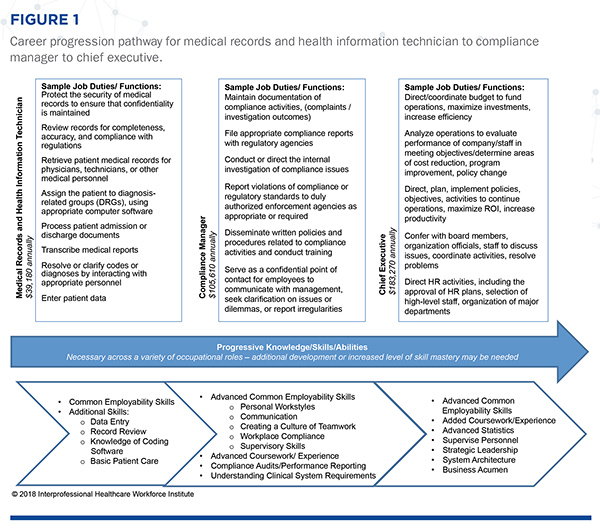
In addition to differentiation in required skills, job descriptions also change in required credentials related to the occupational role. A review of competency domains from several organizations providing credentials for these occupational roles indicates greater specificity to the job roles/functions rather than alignment with the O*NET KSAs. For example, the American Medical Billing Association (CMRS credential) and the American Association of Professional Coders (CPC credential) address KSAs in areas such as medical terminology, information technology, coding, insurance claims, compliance/HIPAA, and managed care. Furthermore, the Health Business Management Association’s (CHBME credential) tests applicant KSAs in areas such as strategic planning, financial management, operations, practice management, customer relations, technology, compliance, and system software/security. These domain areas indicate greater levels of role specificity than KSAs identified by O*NET respondents. Although data was limited, the job descriptions address more specific job tasks and highlight the need for alignment between O*NET KSAs (i.e., perceptions of professionals) and specific role competencies identified by industry representatives. Figure 1 provides a visual representation of career progression pathway opportunities and needed KSAs aligned with job tasks for the medical records and health information technician role to advance to the compliance manager and chief executive within the healthcare organization.
Findings reported in Figure 1 provide further support that as an individual progresses in their career, there is a skills shift from transactional to transformative (from data entry to the use of advanced statistics to interpret data) and from operational to strategic (from retrieving patient records to analyzing operations to enhance business performance in the areas of cost reduction, program improvement, and policy change). This shift underscores the need for common employability skills such as critical thinking, oral and written communication, and judgement and decision making. Conclusion
Resources 2 World Economic Forum. The Future of Jobs: Employment, Skills, and Workforce Strategy for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. January 2016. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs.pdf Accessed May 9, 2018. 3 Heerwaren, J., Kelly, K., and Kampschroer, K. The Changing Nature of Organizations, Work, and Workplace. Accessed May 8, 2018 at: HTTPS; www.wbdg.org/resources/changing-nature-organizations-work-and-workplace. 4 https://www.onetonline.org/ 5 https://www.onetonline.org/link/summary/29-2071.00; https://www.onetonline.org/link/summary/11-9199.02; and https://www.onetonline.org/link/summary/11-1011.00 6 National Network of Business and Industry Associations. Common Employability Skills: A Foundation for Success in the Workplace. 2015. http://nationalnetwork.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/Common_Employability_Skills-03-30-152.pdf 7 AdeccoUSA. Watch the skills gap. May 6, 2018. https://www.adeccousa.com/employers/resources/skills-gap-in-the-american-workforce/ .
|


 Susan Hart-Hester, Ph.D., RHIA, is the director of research at the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She brings over 25 years of experience in the healthcare environment to Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Hart-Hester’s efforts include assisting to position the institute as an industry thought leader in workforce development for the healthcare professions, designing research studies, engaging nationally recognized partners, and developing grant/project proposals that support the institute’s research agenda/priorities and financial goals.
Susan Hart-Hester, Ph.D., RHIA, is the director of research at the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She brings over 25 years of experience in the healthcare environment to Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Hart-Hester’s efforts include assisting to position the institute as an industry thought leader in workforce development for the healthcare professions, designing research studies, engaging nationally recognized partners, and developing grant/project proposals that support the institute’s research agenda/priorities and financial goals.  Rebecca Holton, CFRE, is the director of the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She is responsible for providing strategic direction and management to the institute’s public relations, marketing and communications, and business development. She assists in oversight of institute performance, cultivates and facilitates strategic collaborations with individual, corporate, private, and government partners, and helps guide development of institute programming and initiatives.
Rebecca Holton, CFRE, is the director of the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute, Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She is responsible for providing strategic direction and management to the institute’s public relations, marketing and communications, and business development. She assists in oversight of institute performance, cultivates and facilitates strategic collaborations with individual, corporate, private, and government partners, and helps guide development of institute programming and initiatives.  Kathryn Jackson, RHIA, is the manager of research and education at the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She serves as the manager of research and education for the institute. In this role, she manages projects to ensure timeliness and deliverables are met, including conducting interviews, assisting with focus groups, and compiling responses, and assists in the distribution of program information.
Kathryn Jackson, RHIA, is the manager of research and education at the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. She serves as the manager of research and education for the institute. In this role, she manages projects to ensure timeliness and deliverables are met, including conducting interviews, assisting with focus groups, and compiling responses, and assists in the distribution of program information.  William “Bill” Rudman, Ph.D., RHIA, is the executive director of the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Before moving to Rosalind Franklin, Rudman, served as the executive director of the AHIMA Foundation and vice president of education visioning for the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). Rudman worked for over 20 years in academia as a professor in health information management.
William “Bill” Rudman, Ph.D., RHIA, is the executive director of the Interprofessional Healthcare Workforce Institute Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Before moving to Rosalind Franklin, Rudman, served as the executive director of the AHIMA Foundation and vice president of education visioning for the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). Rudman worked for over 20 years in academia as a professor in health information management. 